Southwest Washington
Overview
Southwest Washington is home to some of the most marine dependent communities in the nation. The local economy relies on healthy waters and intact coastal habitats that support fishing and shellfish aquaculture activities. Fortunately, Washington’s outer coast has avoided many of the negative impacts associated with population growth and urbanization and still contains vast expanses of natural shoreline. In the estuaries and mudflats, shellfish and eelgrass beds provide food and shelter for young Pacific salmon, Dungeness crab, and migratory birds. On land, coastal dunes and forests are a source of high quality habitat for flora and fauna alike. This collection of habitats also buffers the shoreline from storms and flooding, protecting people, property, and infrastructure.
As populations grow, development pressure on coastal habitats may increase along the outer coast. Concurrently, the effects of climate change– sea level rise, flooding, increasing storms, and coastal erosion– cause the shoreline to retreat landward. In a changing environment, habitat conservation is essential so that coastal habitats can continue to deliver their steady stream of benefits. We must create a vision for our shoreline that balances the needs of the community with the needs of the environment so that both can thrive.
Coastal Hazards
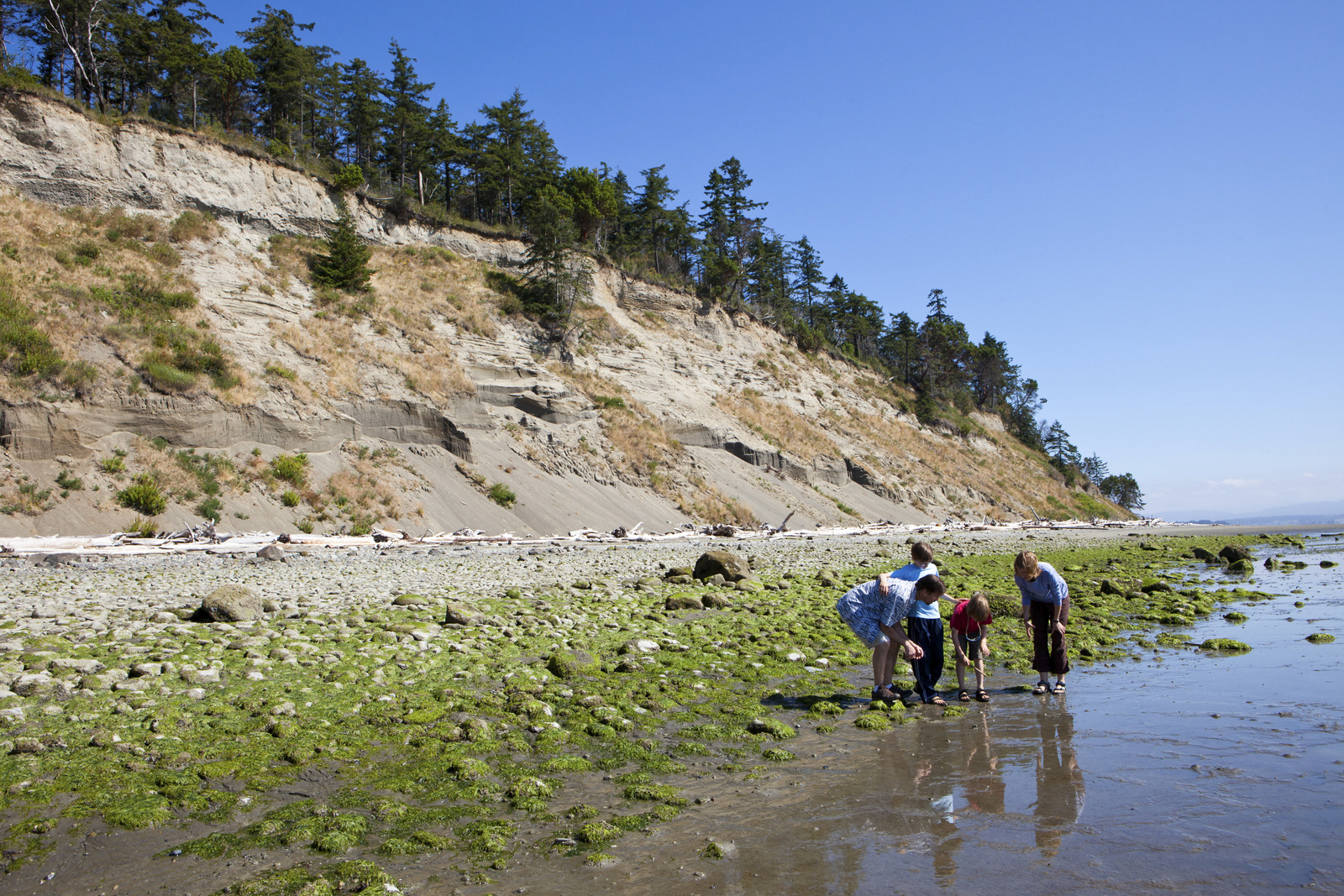
The southwest Washington Coast is subject to inundation and erosional hazards that pose a threat to coastal communities. The sandy beaches and bluffs of Pacific County and Grays Harbor County are particularly vulnerable to erosion due to indirect effects of human activities and natural weather patterns. For example, construction of dams on the Columbia River and jetties at its mouth has altered sediment flow and hydrology of the Columbia River littoral cell. The result is a lack of sediment to replenish beaches as they erode. Erosion of bluffs and shorelines is further intensified during El Niño periods and large storms, when sea levels are higher and wave action is stronger. These impacts can result in significant economic losses to property owners and communities charged to protect the shoreline through mitigation (e.g. installment of geotubes, sandbags, and hardening structures).
Unlike sandy beaches and bluffs that undergo rapid change, estuaries are a transitional buffer between land and sea. Protected estuaries like Grays Harbor and Willapa Bay (Pacific County) receive sediment inputs from surrounding rivers and streams. Eelgrass and other intact shoreline habitats play an essential role in maintaining accretion within estuaries to prevent shoreline erosion by trapping sediments. However, storm events that bring surge, waves, and high river flows can still lead to inundation and erosion in both the Grays Harbor Estuary and Willapa Bay.

North Cove Community Beach. Photo Credit: Kit Swartz
Sea level rise is a certain impact of climate change. As global temperatures increase, rising sea levels on top of storm surges and high tides will intensify flooding and erosion in coastal regions. The National Oceanographic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA)’s regional sea level rise projections for the southwest Washington Coast range from 4-27 cm by 2030, 8-73cm by 2050, and 19-289 cm by 2100 based on a series of future greenhouse gas emission scenarios for the Toke Point tidal gauge station.
Rising seas place coastal communities and ecosystems at risk. A 183 cm (or 6ft.) rise in sea levels could result in the flooding of 9,300 homes in Grays Harbor and 1,700 homes in Pacific County even without the additional factors of a high tide or storm event. The resulting damage to homes and other infrastructure from this level of flooding would be over a billion dollars over the course of the next century.
Rising seas will also cause declines in coastal habitats like eelgrass beds that depend on a narrow optimal depth range and saltmarshes that need room to migrate inland. A decline in these protective habitats may further exacerbate the impacts of erosion and inundation.
Shoreline Armoring

North Cove erosion Cemetery Beach Road. Photo Credit: Kit Swartz
Armoring techniques (e.g. sea walls, jetties, breakwaters, and groins) are sometimes used as a solution to control coastal flooding and erosion. These methods can have negative ramifications on ecosystems by degrading surrounding vegetation and ecological functions, as well as altering sediment transport, hydrology, and channel movement (WAC 173-26-231). Additionally, armored shorelines can prevent the natural shoreline from retreating inland as sea levels rise, leading to loss of important coastal habitats (Figure 1).

Figure 1. Certain ecosystems (e.g., wetlands) can move landward as sea levels rise. The ability of a habitat to move landward depends on several factors including the presence of physical obstacles preventing the subtidal or intertidal habitat from migrating.
Natural Infrastructure
Coastal communities are increasingly interested in using natural habitats and soft stabilization methods to maintain coastal resiliency in the face of a changing environment. Coastal habitats such as eelgrass beds, shellfish beds, saltmarshes (wetlands), sand dunes, and native coastal vegetation are valuable natural resources that can dissipate wave energy, slow water transfer, and stabilize sediments. In the long run, investing in natural habitats (through protection, enhancement, or restoration) can be more cost effective than shoreline armoring as natural systems grow stronger with time, adapt as sea level rise, and self-recover after a storm.

Marsh habitat in Willapa Bay. Photo by Harley Soltes.
Natural habitats also provide other co-benefits that serve the community continually over time. In addition to their ability to buffer shorelines from erosion and flooding, they can serve as nursery grounds for economically important species, improve water quality, and provide recreation opportunities.
Development in vulnerable areas poses a risk to property and habitats, which can have a cascading effect on coastal communities. To increase coastal resiliency, communities can encourage developers to implement setbacks and buffers along the shoreline to reduce risks to infrastructure and the need for shoreline armoring in the future.
To learn more about the role that natural habitats play in protecting infrastructure visit NOAA’s Green Infrastructure website.
Modeling Tools
Coastal Vulnerability-
Spatial modeling tools can help communities see risks of coastal hazards both now and in the future. The Integrated Valuation of Environmental Services and Tradeoffs (InVEST) Coastal Vulnerability model (created by the Natural Capital Project) is one tool that can help communities understand how their shorelines are vulnerable to storms and the role that habitat plays in buffering shorelines from the impacts of erosion and inundation. The model was run for Pacific County and Grays Harbor and the results are located on the Coastal Resilience Mapping Portal under the “Regional Planning” application for the Outer Coast. This tool will allow communities to:
- Identify coastlines currently vulnerable to erosion and flooding due to storm surge and waves (called exposure), and
- Highlight the areas where vulnerability is reduced due to the presence of natural habitats (called habitat role).
The model estimates how vulnerable different areas of the shoreline are to erosion and inundation during coastal storms. Shorelines considered highly vulnerable are those that are most likely to experience erosion and inundation. That vulnerability is a based on five characteristics of the shoreline – 1) Its geomorphology, 2) Surrounding coastal habitats that may or may not buffer the shoreline, 3) Its exposure to wind and waves, 4) The surge potential, 5) And the surrounding relief. Each of these characteristics are ranked for the shoreline segment, and those ranks are then combined and rescaled to produce an index of vulnerability (called exposure) from low to high.
The results can be used to inform the creation of policies and regulations on buffers for local development plans, educate developers and homeowners on the importance of coastal habitats for shoreline protection, and guide restoration activities. By preserving the ecological functions of county shorelines, southwest Washington has the opportunity to work towards resiliency in the face of a changing coastline.
Coastal Vulnerability Mapping Portal:
InVEST Coastal Vulnerability Report:
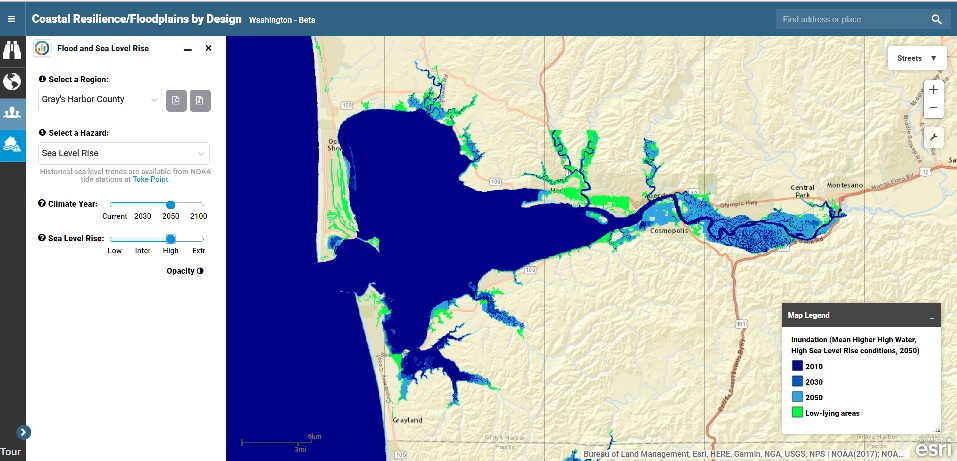
Sea Level Rise-
When scientists and agencies produce advanced sea level rise projections, we can use GIS to create maps of where water will flood inland as seas rise. This can be very helpful for coastal planners as they consider the safest places to develop and where to conserve habitats to utilize their protective services.
Sea level rise mapping simulates where land areas that currently do not get covered by tides may become underwater as sea levels rise. For the tidal regions of Grays Harbor County and Pacific County in southwest Washington, The Nature Conservancy mapped areas that were underwater when tides reached the “Mean Higher High Water” (MHHW) line in 2010 and which may be underwater by 2030, 2050, and 2100 according to NOAA’s 2017 projections of sea level rise at the Toke Point tidal gauge station. These projections can be used as a starting point for visualizing what areas of Pacific and Grays Harbor counties may become inundated as sea levels rise.

Flooding at Ellsworth Slough. Photo by Dave Ryan
Advances in sea level rise projections are currently underway in Washington. Through the Washington Coastal Resilience Project (WCRP) Sea Grant and others are working on innovating sea level rise projections for Washington by:
- Communicating the full range of possible sea level rise in a probabilistic framework.
- Assessing the vertical land movement in Washington to refine projections.
- Analyze and understand the interaction of extreme storm events with sea level rise.
Once complete, these results will improve the ability of communities to forecast and convey the impacts of sea level rise.
Sea Level Rise Mapping Portal for Washington: