Economics of Coastal Adaptation
What is the Economics of Coastal Adaptation app?
![]() Economics of Coastal Adaptation allows you to explore current and future risks from coastal hazards and to compare the cost-effectiveness of nature-based (green), artificial (gray), and policy solutions to reduce risks and avert damages across the Gulf of Mexico. It helps us understand what drives coastal risk and helps to inform adaptation decisions.
Economics of Coastal Adaptation allows you to explore current and future risks from coastal hazards and to compare the cost-effectiveness of nature-based (green), artificial (gray), and policy solutions to reduce risks and avert damages across the Gulf of Mexico. It helps us understand what drives coastal risk and helps to inform adaptation decisions.
Main functions:
- Visualize the value of residential, commercial, industrial, and essential facilities assets in low elevation areas by county or census tract.
- Assess future risk to flood and wind hazards by evaluating expected damage from storms under various economic growth and climate scenarios..
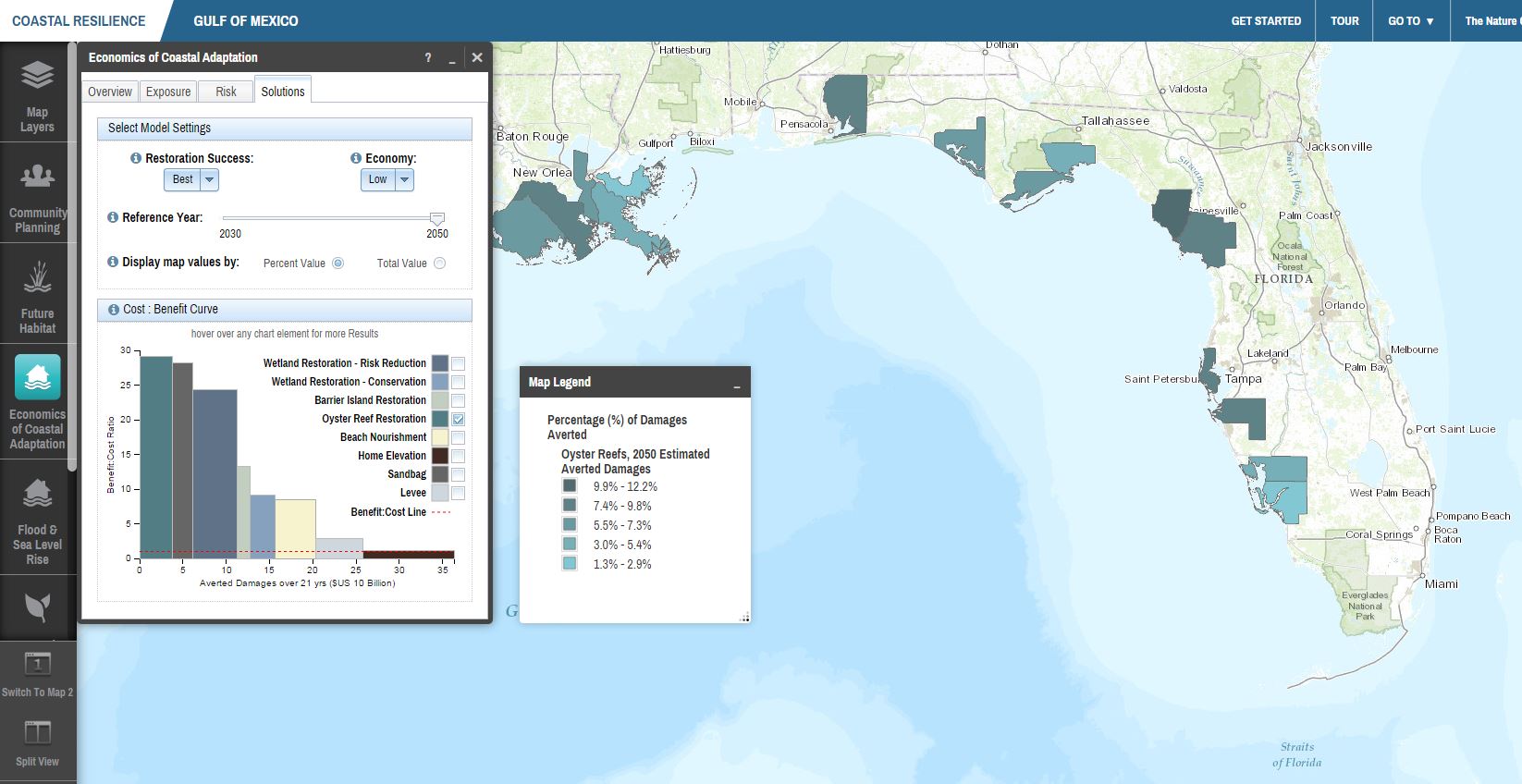
- Compare the cost effectiveness of 8 different natural and artificial solutions, ranging from habitat restoration to home elevation, by evaluating how much flood damage each solution could avert in relation to how much it would cost to implement.
Who should use it?
Risk assessments and cost-benefit analyses that incorporate natural defenses are relevant for insurers, lenders, agencies, and communities that are seeking viable and cost-effective solutions for reducing risk.

Judy Haner, Marine Program Director at TNC in Alabama, speaks with a local fisherman. Photo credit: Andrew Kornylak
How does it work?

Economics of Coastal Adaptation User Interface
The app uses Climada, an open-source risk model developed by the Economics of Climate Adaptation working group and expanded by the reinsurance company Swiss Re in partnership with The Nature Conservancy and UC Santa Cruz. Climada stands for climate adaptation and is a probabilistic natural catastrophe damage model that calculates averted damage (benefit) of green and grey adaptation solutions.
Where is it being used?
The app is currently being used in the Gulf of Mexico to demonstrate that future risks from coastal hazards will be significant and to illustrate that a suite of cost effective solutions, including nature based defenses, can reduce risk and avert damages for millions of people in the region. To date, oyster reef and marsh restoration have been identified as some of the most cost effective solutions for risk reduction. The ECA app helped determine that nature-based defenses alone could help avert more than $50 billion in damages over a 20-year period in the Gulf of Mexico. The cost-effectiveness of adaptation solutions depends significantly on where these projects are done, which should influence regional priorities.

Photo credit: Carlton Ward/The Nature Conservancy
Launch the Economics of Coastal Adaptation app in the Gulf of Mexico’s mapping portal.
Who helped develop it?
The Nature Conservancy has long been active in all of the states on the Gulf Coast protecting and restoring critical habitats. Through the Conservancy’s decade-long partnership with the NOAA Restoration Center, and more recently with support from the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act, we have jointly invested millions of dollars in the restoration of Gulf oyster reefs, seagrass beds, coastal wetlands, coral reefs, and barrier islands.
The Swiss Re Group is a leading wholesale provider of reinsurance, insurance and other insurance-based forms of risk transfer. They have been working with TNC to assess the cost-effectiveness of both nature-based and artificial risk reduction strategies using their industry-based open-source risk models.
The Economics of Climate Adaptation Working Group, a partnership between the Global Environment Facility, McKinsey & Company, Swiss Re, the Rockefeller Foundation, ClimateWorks Foundation, the European Commission, and Standard Chartered Bank.
What are the strengths?
- The integrated nature-based approach helps leverage the capacity of wetlands, beaches and dunes, reefs, and other natural features to reduce the impacts of storm surge and waves.
- The information presented in the ECA app can help societies better understand the climate risk to their economies and provide vital input into impactful, cost-effective adaptation strategies that boost overall economic development.